“Once bond principal and interest payments are made, the leftover profits are retained by shareholders and can be paid out in the form of dividends or buybacks,” Fiorica says. “Therefore, a lower debt-to-equity ratio implies that equity holders have a greater chance of benefiting from growth in retained earnings over time and a lower risk of default.” A high D/E ratio indicates that a company has been aggressive in financing its growth with debt. While this can lead to higher returns, it also increases the company’s financial risk.
Role of Debt-to-Equity Ratio in Company Profitability
Banks also tend to have a lot of fixed assets in the form of nationwide branch locations. To get a sense of what this means, the figure needs to be placed in context by comparing it to competing companies. The following D/E ratio calculation is for Restoration Hardware (RH) and is based on its 10-K filing for the financial year ending on January 29, 2022. Of note, there is no “ideal” D/E ratio, though investors generally like it to be below about 2. It’s easy to get started when you open an investment account with SoFi Invest. You can invest in stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, alternative funds, and more.
Ask Any Financial Question
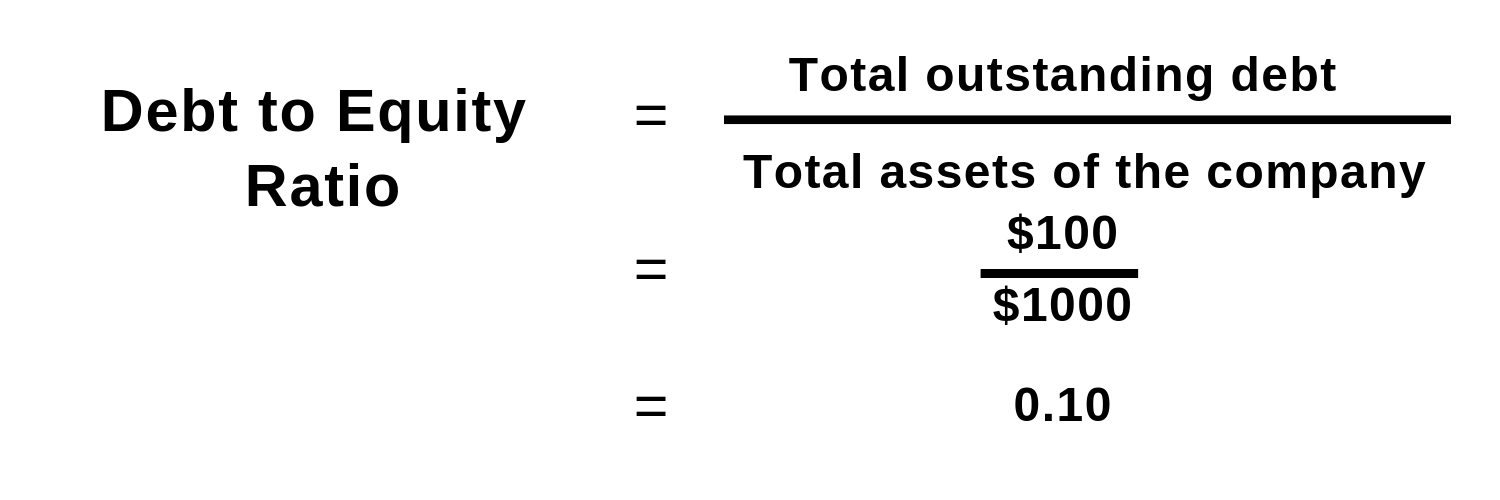
The debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio is a metric that provides insight into a company’s use of debt. What is considered a high ratio can depend on a variety of factors, including the company’s industry. The debt to equity ratio is calculated by dividing total liabilities by total equity.
What Is Leverage?
- As a result, borrowing that seemed prudent at first can prove unprofitable later under different circumstances.
- A lower debt to equity ratio usually implies a more financially stable business.
- Microsoft Excel provides a balance sheet template that automatically calculates financial ratios such as the D/E ratio and the debt ratio.
- SoFi doesn’t charge commissions, but other fees apply (full fee disclosure here).
And a high debt-to-equity ratio can limit a company’s access to borrowing, which could limit its ability to grow. The interest rates on business loans can be relatively low, and are tax deductible. That makes debt an attractive way to fund business, especially compared to the potential returns from the stock market, which can be volatile. For example, if a company, such as move from excel to accounting software a manufacturer, requires a lot of capital to operate, it may need to take on a lot of debt to finance its operations. Current liabilities are the debts that a company will typically pay off within the year, including accounts payable. Not all debt is considered equally risky, however, and investors may want to consider a company’s long-term versus short-term liabilities.
They can also issue equity to raise capital and reduce their debt obligations. A negative D/E ratio indicates that a company has more liabilities than its assets. This usually happens when a company is losing money and is not generating enough cash flow to cover its debts. When it comes to choosing whether to finance operations via debt or equity, there are various tradeoffs businesses must make, and managers will choose between the two to achieve the optimal capital structure. A high D/E ratio suggests that the company is sourcing more of its business operations by borrowing money, which may subject the company to potential risks if debt levels are too high. From the above, we can calculate our company’s current assets as $195m and total assets as $295m in the first year of the forecast – and on the other side, $120m in total debt in the same period.
Debt to Equity Ratio Formula & Example
Its debt-to-equity ratio would therefore be $1.2 million divided by $800,000, or 1.5. If its assets provide large earnings, a highly leveraged corporation may have a low debt ratio, making it less hazardous. Contrarily, if the company’s assets yield low returns, a low debt ratio does not automatically translate into profitability.
While the total debt to total assets ratio includes all debts, the long-term debt to assets ratio only takes into account long-term debts. The term debt ratio refers to a financial ratio that measures the extent of a company’s leverage. The debt ratio is defined as the ratio of total debt to total assets, expressed as a decimal or percentage. It can be interpreted as the proportion of a company’s assets that are financed by debt.
A debt due in the near term could have an outsized effect on the debt-to-equity ratio. So in the case of deciding whether to invest in IPO stock, it’s important for investors to consider debt when deciding whether they want to buy IPO stock. In order to calculate the debt-to-equity ratio, you need to understand both components.
Generally speaking, a high ratio may indicate that the company is much resourced with (outside) borrowing as compared to funding from shareholders. The current ratio reveals how a company can maximize its current assets on the balance sheet to satisfy its current debts and other financial obligations. This tells us that Company A appears to be in better short-term financial health than Company B since its quick assets can meet its current debt obligations.
Debt financing is often seen as less risky than equity financing because the company does not have to give up any ownership stake. There are various companies that rely on debt financing to grow their business. For example, Nubank was backed by Berkshire Hathaway with a $650 million loan. A good D/E ratio also varies across industries since some companies require more debt to finance their operations than others. A low D/E ratio shows a lower amount of financing by debt from lenders compared to the funding by equity from shareholders. The D/E ratio indicates how reliant a company is on debt to finance its operations.
